Rambla Salvador Samà, 47
Vilanova i la Geltrú – Barcelona
CONTACT FORM

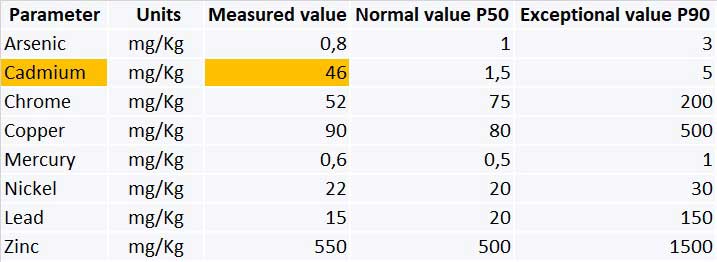
Heavy metals are metals whose density is at least five times that of water. They are toxic and cause damage to health when their concentration in the environment is excessive .
Sometimes they are detected in dust in homes and offices. The following list details the most problematic heavy metals and where they can be found:


Their effects are often difficult to relate to their presence, since their polluting power is cumulative, not immediate and does not affect all people equally.
In general, heavy metals can cause a wide range of disease symptoms: liver and kidney damage, nervous disorders, infections, allergies, anemia, bone deformities and cancer. They do not degrade in the body, but are deposited and accumulate in the kidneys, bones or skin (especially in the subcutaneous fatty tissue).
Each metal also has its own peculiarities, e.g. lead impairs reproductive capacity: it decreases sperm and increases premature births and miscarriages. Fortunately, outdoor levels have decreased with the advent of unleaded petrol.

In case of suspicion of environmental illness, such as multiple chemical sensitivity or fibromyalgia, for example, or previous detection of heavy metals in blood tests, measurement in household and/or office dust is advised.
The next step is to look for possible sources of the measured elements. If necessary, surface samples of the suspected material can be taken and analysed.
Once the sources are located, they should be eliminated. Each metal has its own procedure.
For example, mercury spilled from a broken thermometer should be immediately placed in a sealed plastic bag and taken to a special waste collection point. It should never be removed with a broom or vacuum cleaner, as it is more quickly spread by dust and even indoor air, which can aggravate the problem.
Rambla Salvador Samà, 47
Vilanova i la Geltrú – Barcelona

2024 © Copyright - Carles Surià